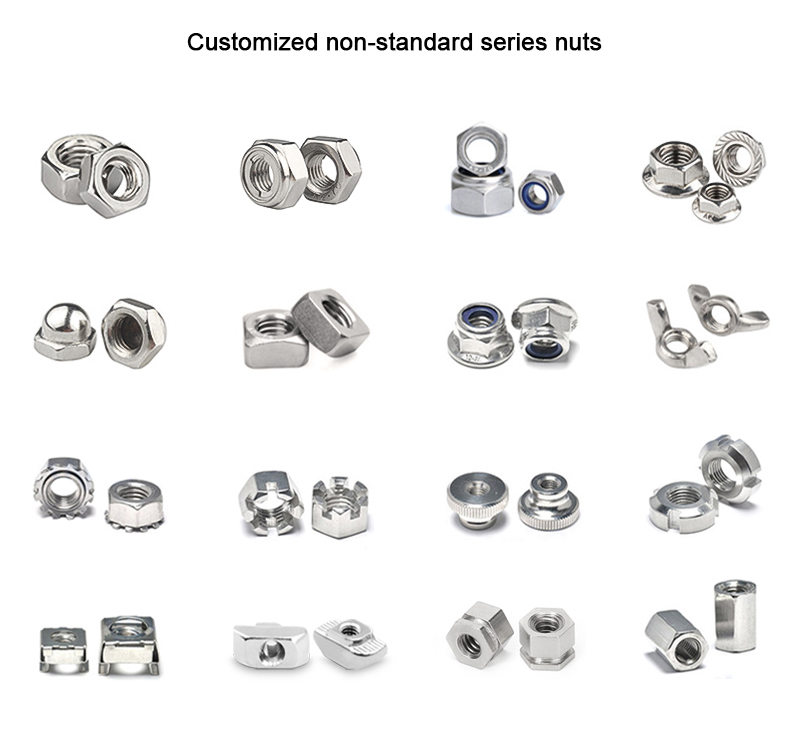
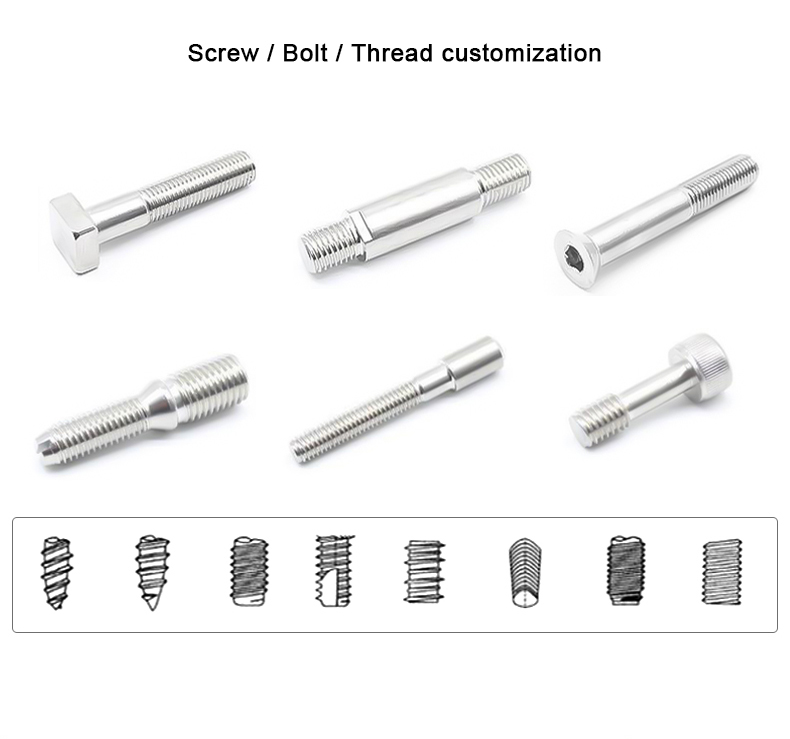




O processo de encabeçamento a frio é um dos novos processos para a maquinagem sob pressão com menos ou nenhum corte
metal. É um método de processamento que utiliza a deformação plástica do metal sob a ação de
forças externas e, com a ajuda de moldes, redistribui e transfere o volume de metal para formar
as peças ou os espaços em branco necessários. O processo de encabeçamento a frio é o mais adequado para a produção de
elementos de fixação, tais como cavilhas, parafusos, porcas, rebites, cavilhas, etc.

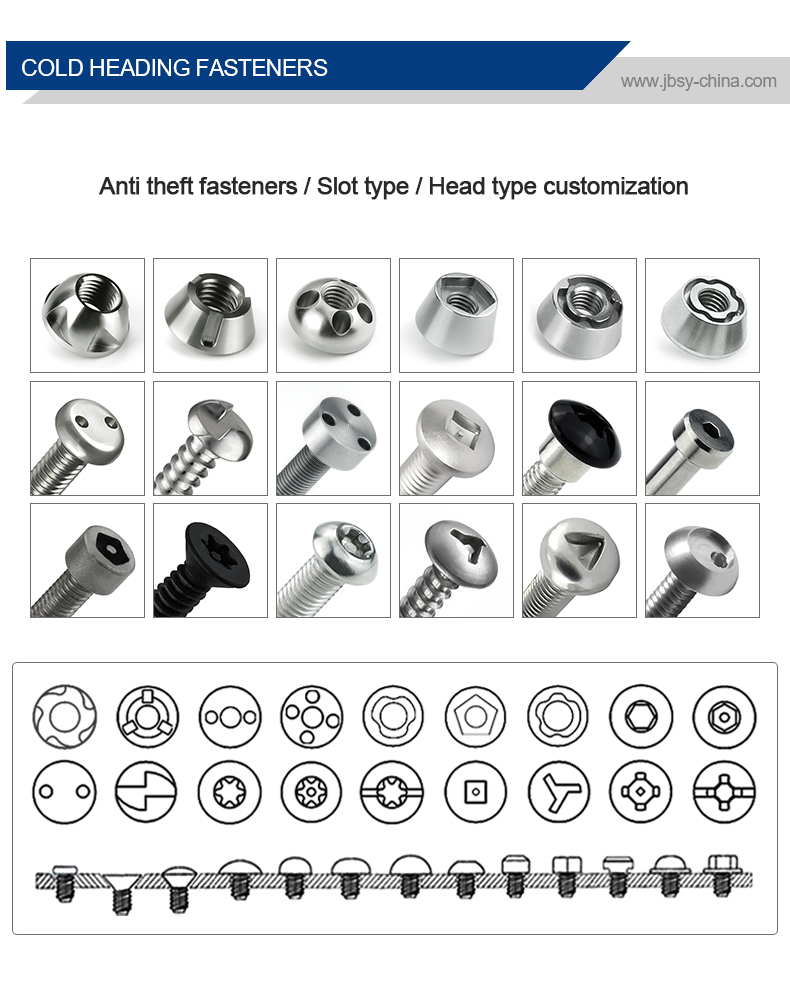
Latão parafusos de cisalhamento são fixadores especializados concebidos para quebrar ou "cisalhar" com um binário pré-determinado ou sob condições de tensão específicas. São normalmente utilizados em aplicações em que o aperto excessivo pode danificar componentes ou em que é necessária resistência à manipulação. Eis uma descrição pormenorizada:
Caraterísticas dos parafusos de cisalhamento de latão:
-
Material:
-
Fabricado em latão (frequentemente com chumbo para poder ser maquinado), oferece resistência à corrosão, condutividade eléctrica e propriedades anti-faiscantes.
-
O latão é mais macio do que o aço, o que o torna ideal para aplicações de cisalhamento.
-
-
Conceção:
-
Ranhura de corte: Uma secção pré-enfraquecida (pescoço) perto da cabeça que se rompe quando o binário excede um limite definido.
-
Cabeça hexagonal ou Torx: Permite apertar até ao corte do parafuso, deixando uma superfície de rutura lisa e resistente à manipulação.
-
Tipo de rosca: Normalmente, as roscas de máquina (por exemplo, métricas ou UNC/UNF) para uma fixação segura antes do corte.
-
-
Função:
-
Limitação do binário: Evita a sobrecarga ao partir com um binário calibrado.
-
Inviolável: Uma vez que a cabeça é cortada, o parafuso não pode ser facilmente removido sem ferramentas especializadas.
-
-
Aplicações:
-
Equipamento elétrico: Ligações de terra, barramentos (para evitar a sobrecompressão).
-
Dispositivos de segurança: Painéis invioláveis, tampas de acesso.
-
Aeroespacial e automóvel: Montagens críticas que requerem um binário preciso.
-
Sistemas de canalização/gás: O metal macio evita a formação de faíscas em ambientes inflamáveis.
-
-
Vantagens:
-
Evita danos provocados por força excessiva.
-
Detém o acesso não autorizado.
-
Resistente à corrosão em ambientes húmidos/exteriores.
-
-
Desvantagens:
-
Não reutilizável após o corte.
-
Menor resistência ao cisalhamento em comparação com os parafusos de aço.
-
Especificações comuns:
-
Normas: DIN, ASTM ou específicos do sector (por exemplo, MIL-SPEC).
-
Graus: Varia consoante a liga (por exemplo, latão C360 para maquinabilidade).
-
Torque de cisalhamento: Personalizável com base no desenho da ranhura e na espessura do material.
Notas de instalação:
-
Utilize uma chave dinamométrica para garantir o corte correto.
-
Após o corte, a haste restante pode necessitar de um extrator de parafusos para ser removida.






