



El proceso de estampado en frío es uno de los nuevos procesos de mecanizado a presión de menor o ningún corte
Se trata de un método de transformación que utiliza la deformación plástica del metal bajo la acción de los agentes atmosféricos.
fuerzas externas y, con ayuda de moldes, redistribuye y transfiere el volumen de metal para formar
las piezas o formatos necesarios. El proceso de estampación en frío es el más adecuado para producir piezas estándar.
elementos de fijación como pernos, tornillos, tuercas, remaches, pasadores, etc.

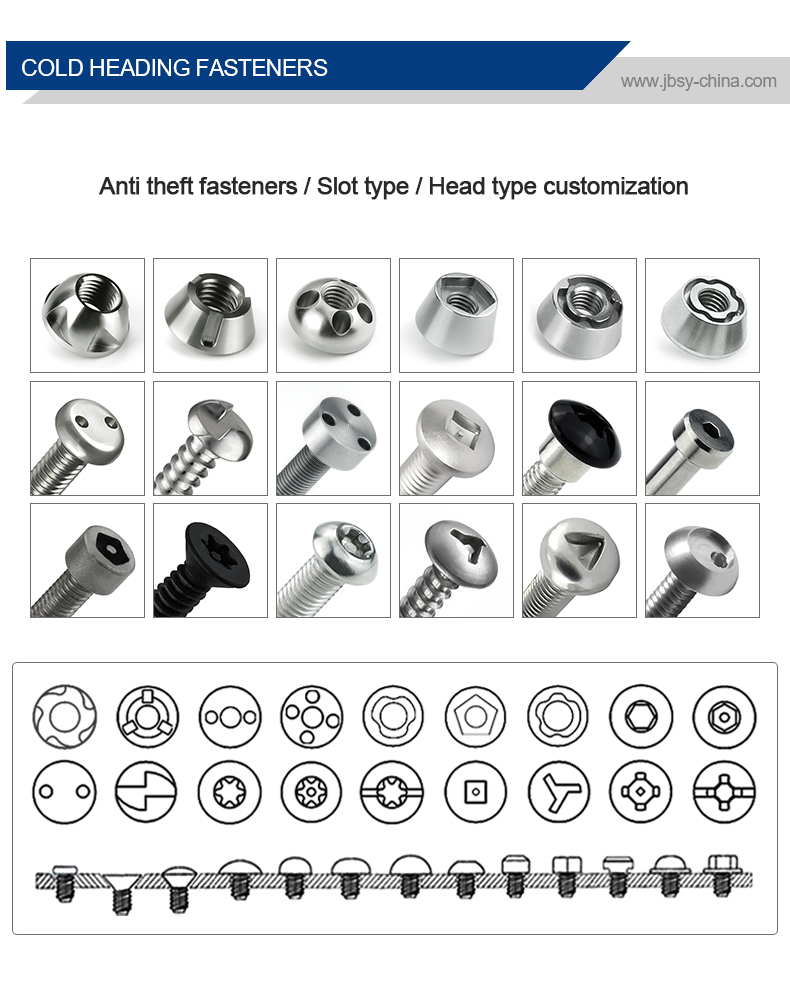
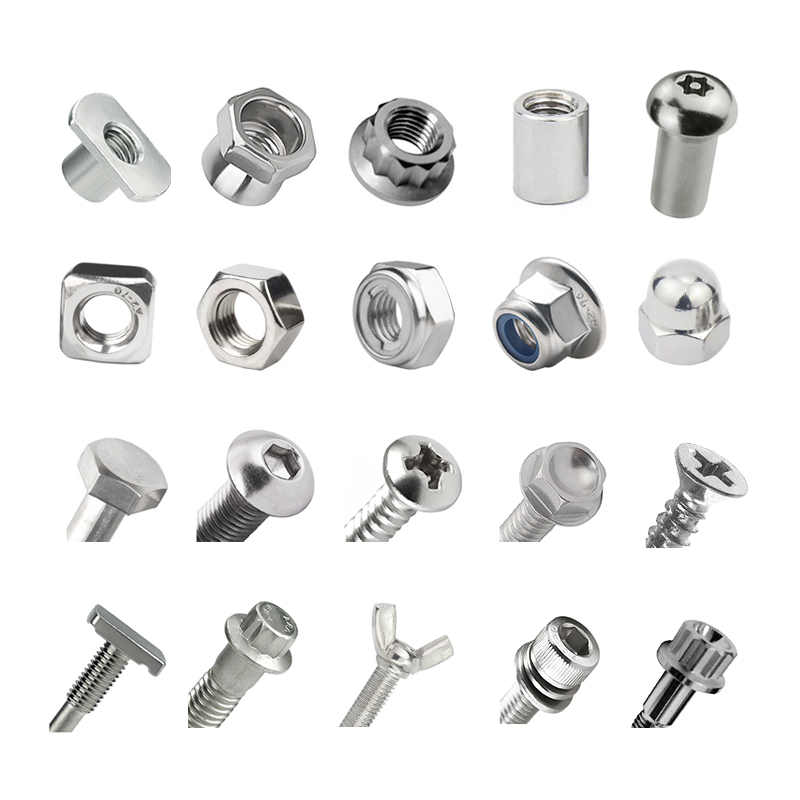
Tuercas y tornillos fabricantes son empresas especializadas en la producción de elementos de fijación, que son componentes esenciales utilizados para unir o asegurar materiales en diversas industrias. Estos fabricantes producen una amplia gama de tuercas, pernos, tornillos, arandelas y otros productos de fijación relacionados, destinados a sectores como la construcción, la automoción, la industria aeroespacial, la maquinaria y los bienes de consumo.
1. Gama de productos:
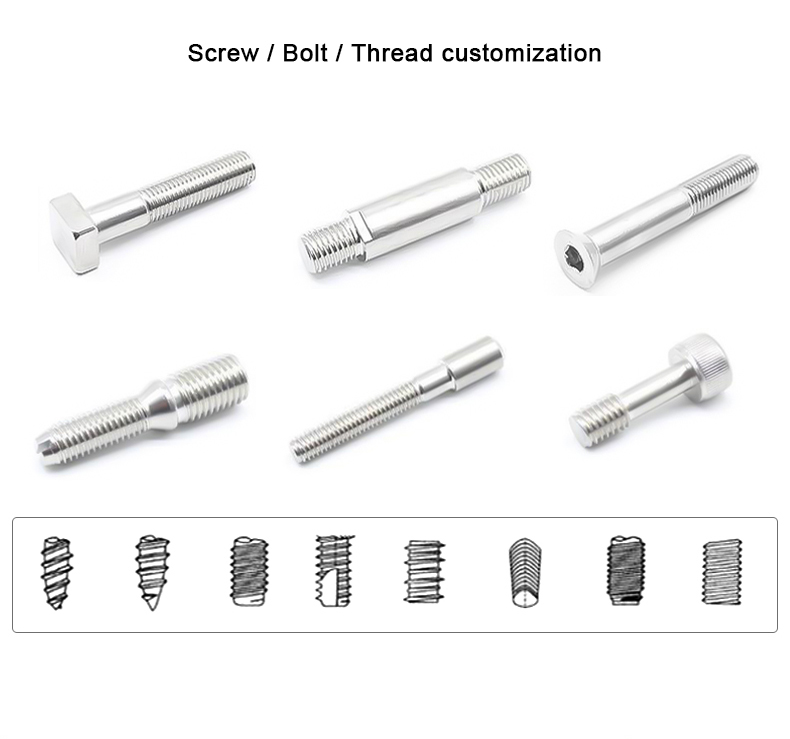
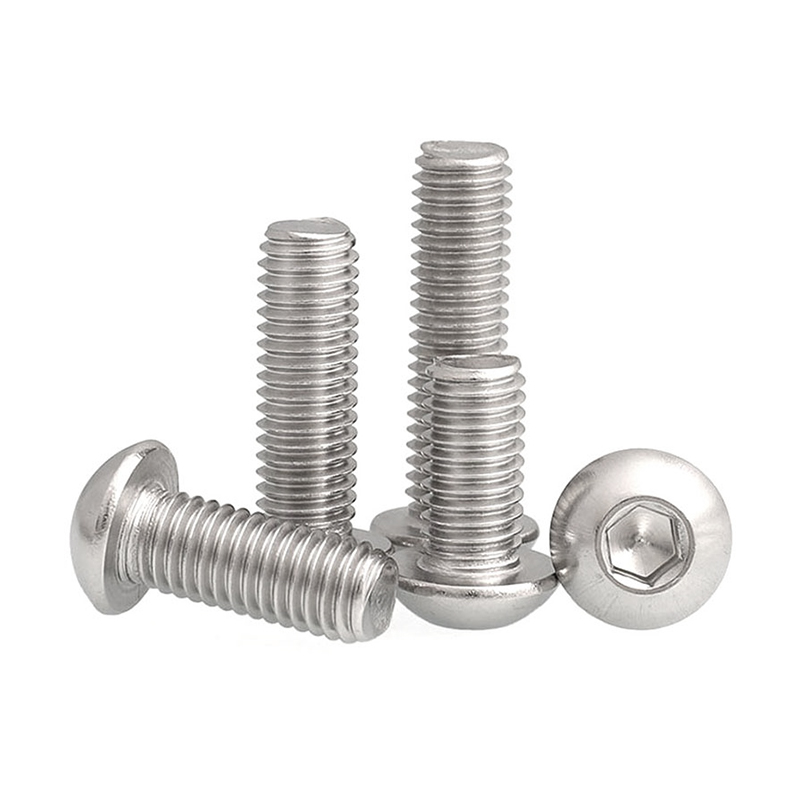
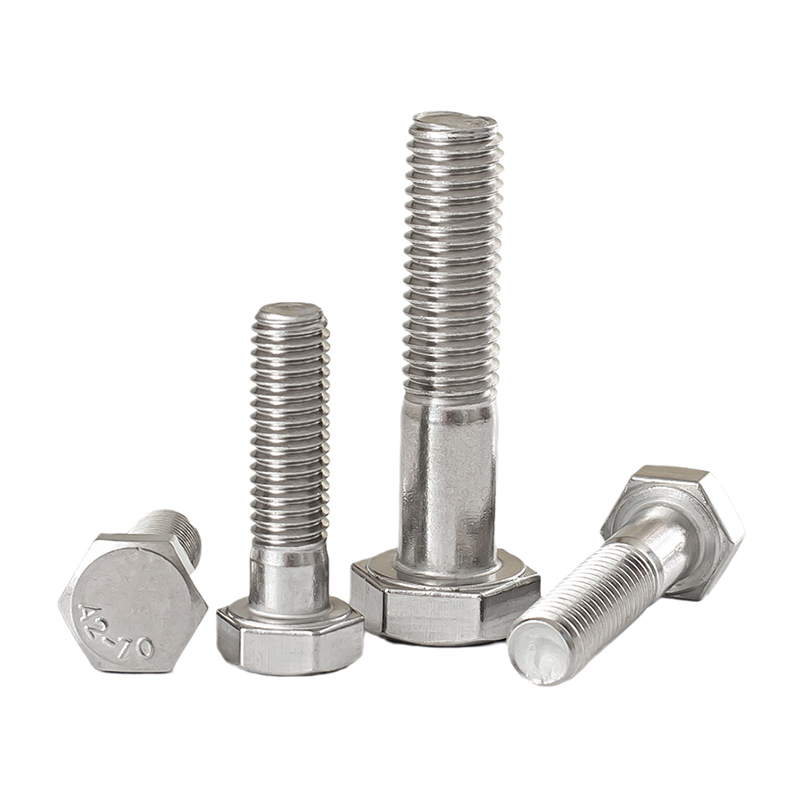
- Pernos: Suelen ser elementos de fijación metálicos con un eje roscado y una cabeza en un extremo. Los tipos más comunes son los pernos hexagonales, los pernos de carro, los pernos de máquina, los tirafondos y los pernos de anclaje.
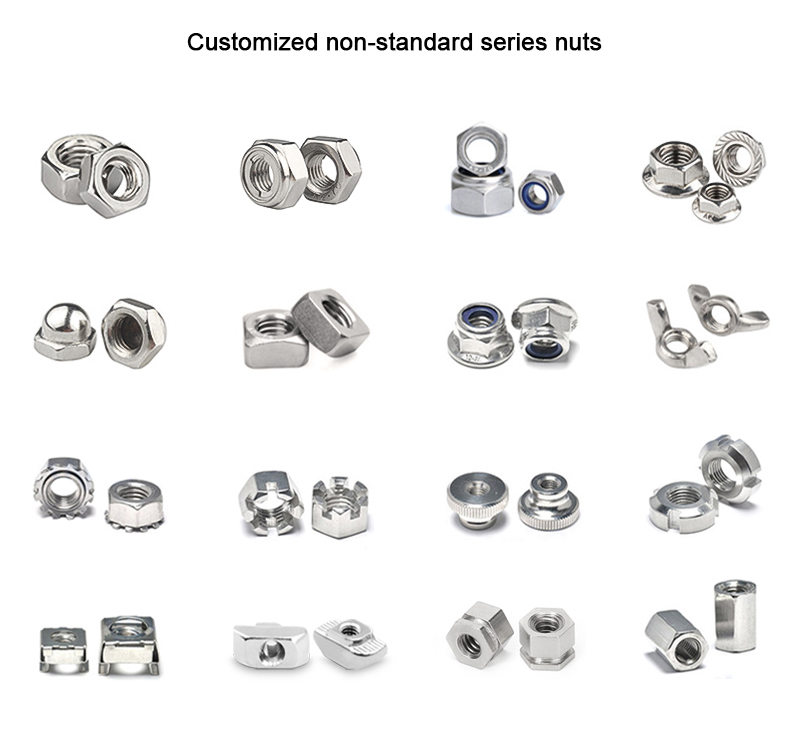
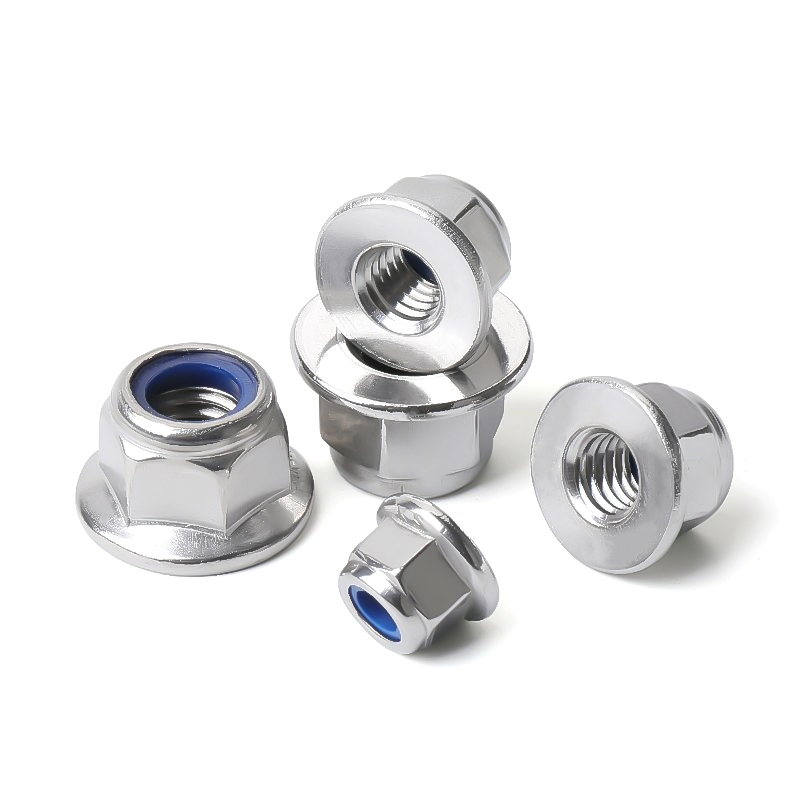
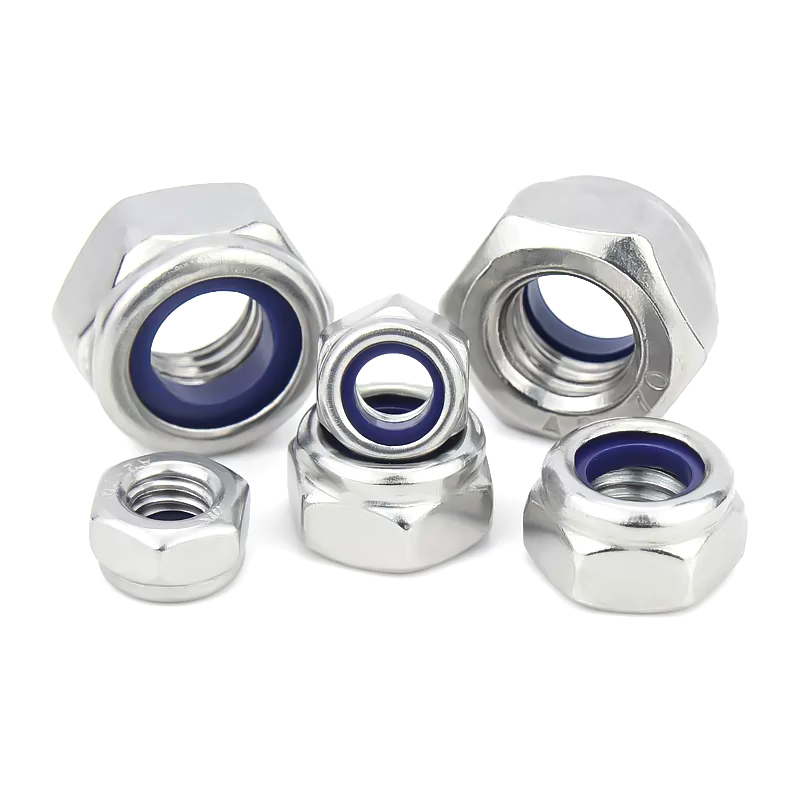
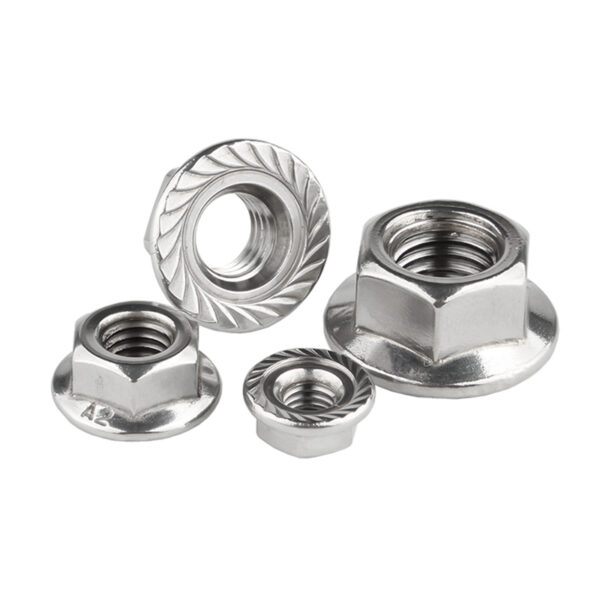
- Nueces: Las tuercas son elementos de fijación con rosca interior que se acoplan a los tornillos. Los tipos más comunes son las tuercas hexagonales, las contratuercas, las tuercas de mariposa y las tuercas de sombrerete.
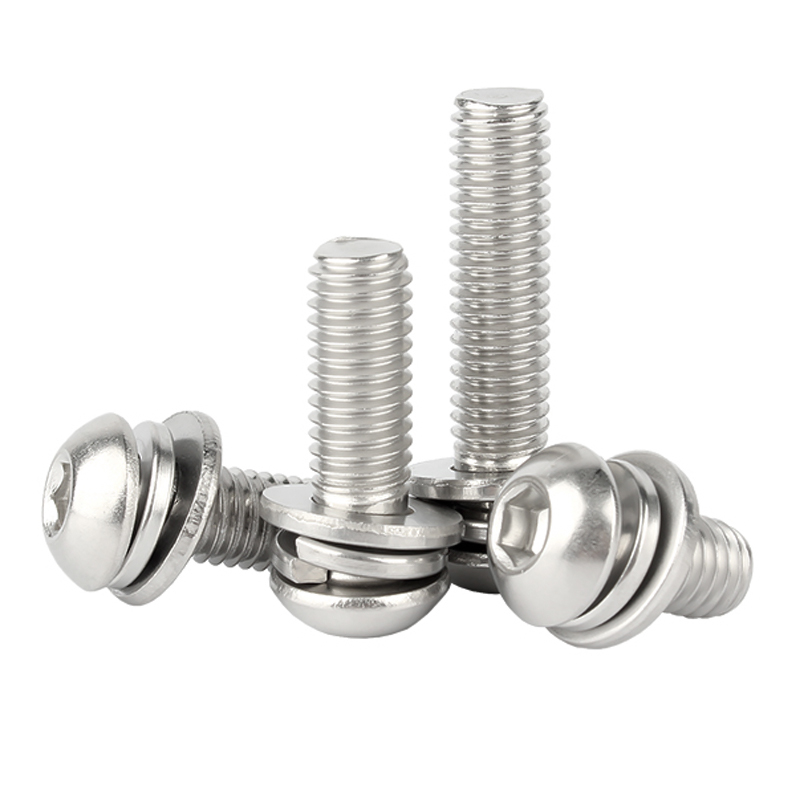
- Lavadoras: Se utilizan con tuercas y tornillos para distribuir la carga y reducir el desgaste. Los tipos incluyen arandelas planas, arandelas elásticas y arandelas de seguridad.
- Tornillos: Aunque ligeramente diferentes de los pernos, los tornillos son otro elemento de fijación roscado que los fabricantes pueden producir.
2. Tipos de material:
- Acero: El material más común, a menudo utilizado en automoción, construcción y aplicaciones industriales.
- Acero inoxidable: Conocido por su resistencia a la corrosión, se utiliza en la industria marina, alimentaria y médica.
- Latón: Proporciona una excelente resistencia a la corrosión y conductividad eléctrica, a menudo utilizado en aplicaciones eléctricas.
- Aluminio: Ligero y resistente a la corrosión, se utiliza en industrias como la aeroespacial.
- Aleaciones especiales: Los fabricantes suelen ofrecer tuercas y tornillos fabricados con materiales como titanio, cobre o aleaciones especiales para satisfacer requisitos específicos de resistencia a la fuerza, la temperatura o los productos químicos.
3. Personalización:
Muchos fabricantes ofrecen tornillos y tuercas a medida adaptados a tamaños, diseños y especificaciones concretos. Esto puede incluir patrones de rosca únicos, revestimiento o características adicionales como formas, tamaños o acabados no estándar.
4. Procesos de fabricación:
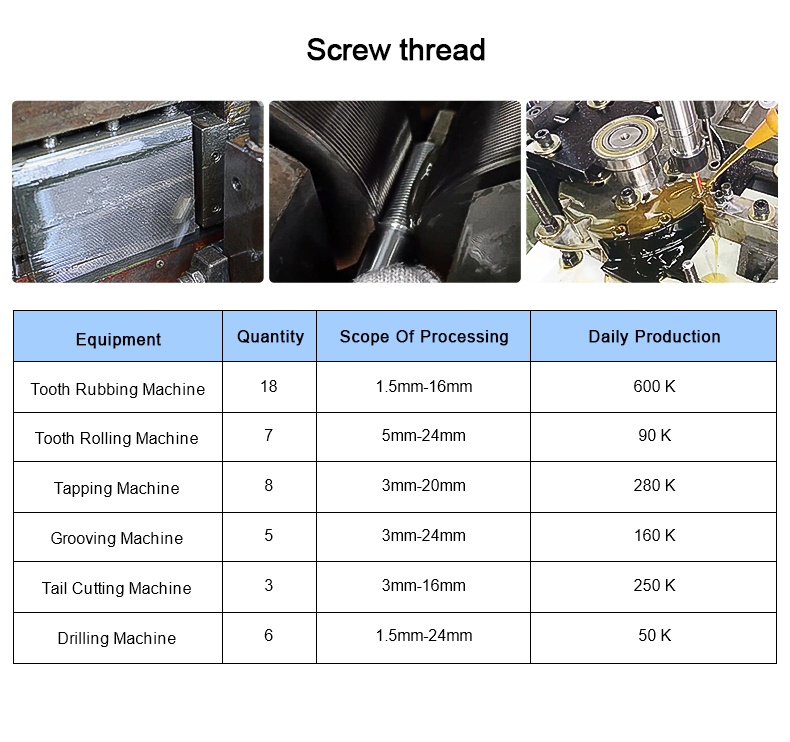
- Rumbo frío: Consiste en formar la cabeza del tornillo a partir de un trozo de alambre sin calentar el material.
- Forja: Se calienta el metal y se le da forma de tornillo o tuerca.
- Hilo rodante: En lugar de cortar roscas, el laminado de roscas forma roscas mediante presión, creando elementos de fijación más resistentes.
- Moldeo por inyección: Para las tuercas y tornillos de plástico, los fabricantes utilizan el moldeo por inyección para darles la forma requerida.
5. Calidad y normas:
Los fabricantes deben cumplir varias normas industriales para garantizar que sus productos cumplen las especificaciones exigidas. Esto incluye:
- Normas ISO (por ejemplo, ISO 9001 para la gestión de la calidad)
- ANSI (Instituto Nacional Estadounidense de Normalización) normas
- ASTM (Sociedad Americana de Pruebas y Materiales) normas relativas a las propiedades de los materiales
- DIN (Instituto Alemán de Normalización) normas (especialmente en Europa)
6. Acabados y revestimientos:
- Cincado: Ofrece resistencia a la corrosión.
- Galvanización: Revestimiento de zinc aplicado por inmersión en caliente para proteger contra la oxidación.
- Anodizado: Se utiliza en fijaciones de aluminio para aumentar la resistencia a la corrosión.
- Revestimiento de fosfato: Añade una capa para una mejor lubricación durante el montaje y aumenta la resistencia a la corrosión.
7. Cadena de suministro:
- Pedidos al por mayor: Muchos fabricantes suministran elementos de fijación a granel para proyectos a gran escala o series de producción.
- Pedidos a medida: También pueden atender pedidos más pequeños o personalizados en función de los requisitos de cada proyecto.
- Distribución mundial: Los grandes fabricantes suelen realizar envíos a todo el mundo, con centros de distribución y asociaciones minoristas en varias regiones.







Valoraciones
No hay valoraciones aún.