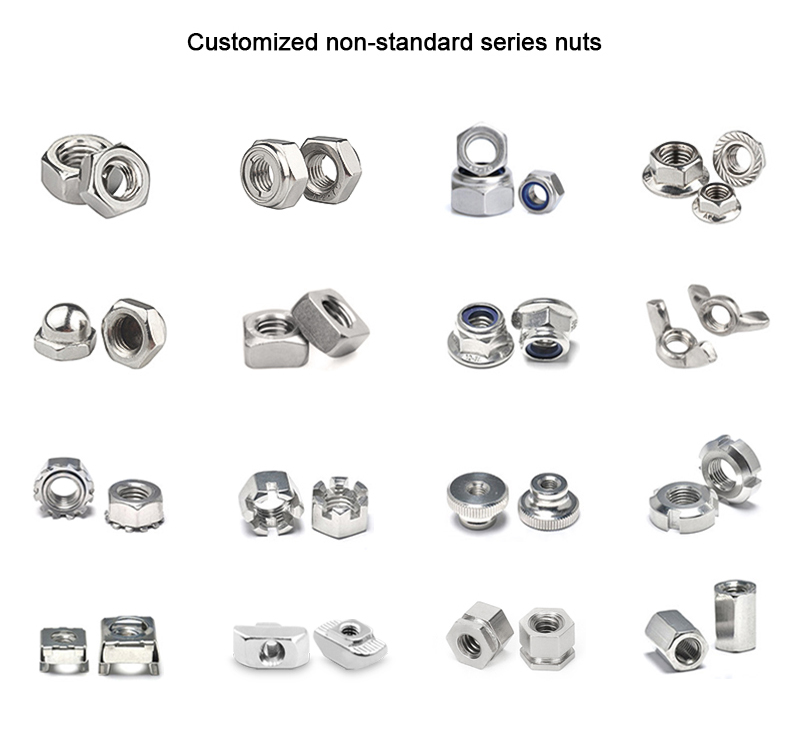
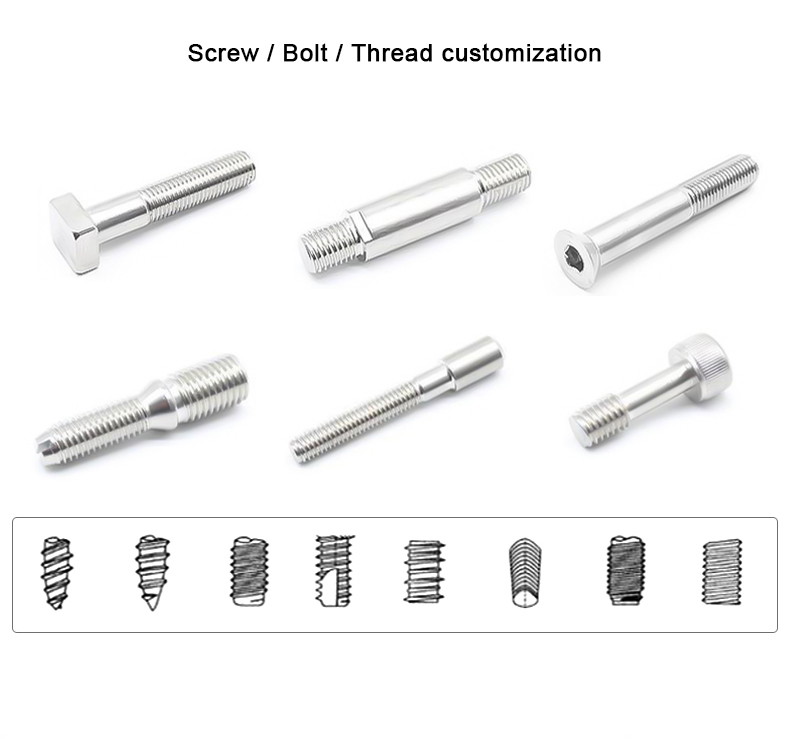

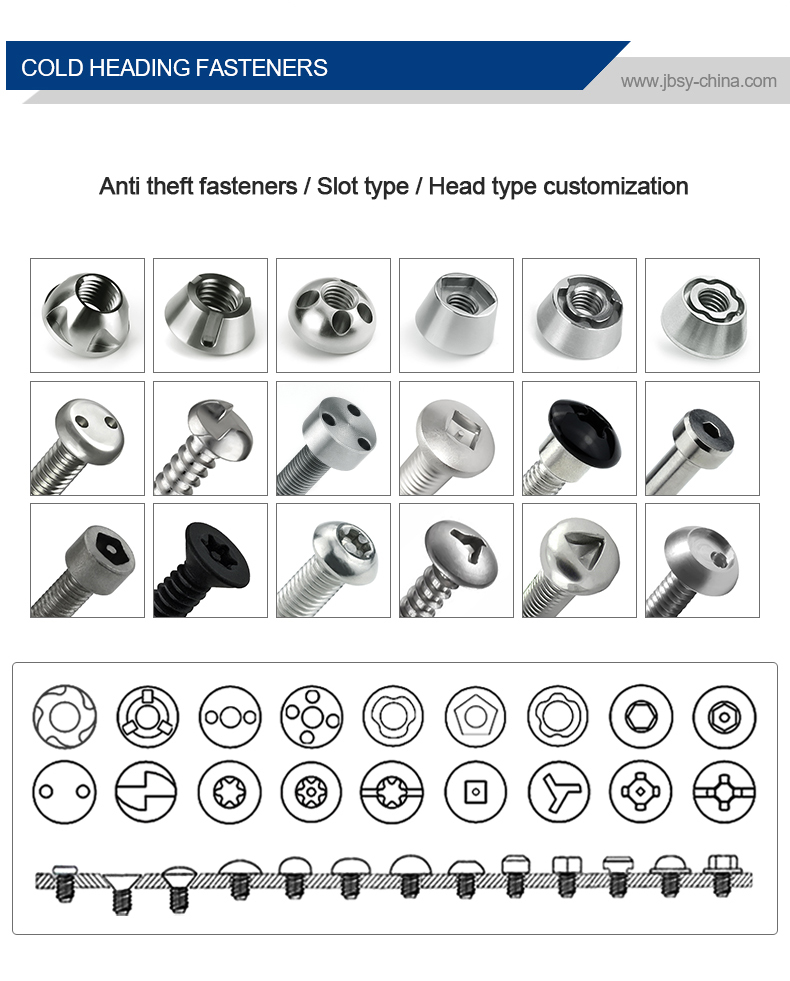



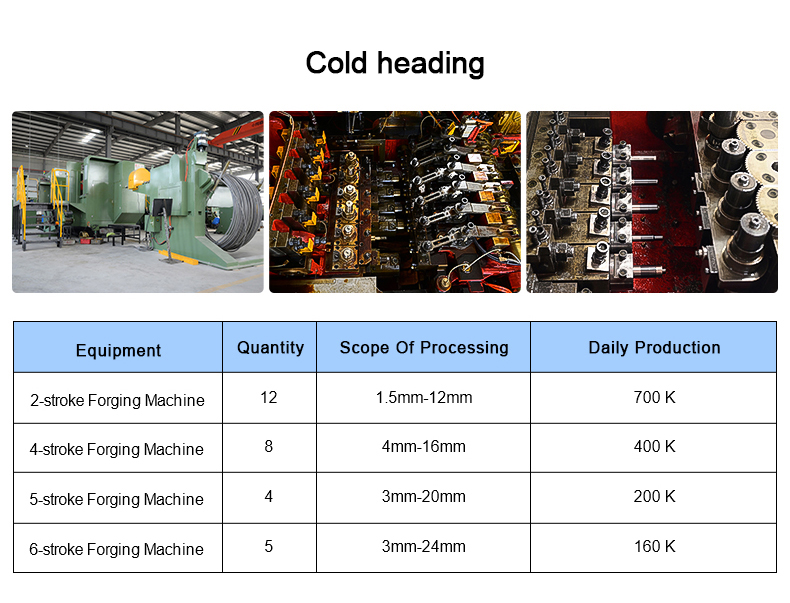
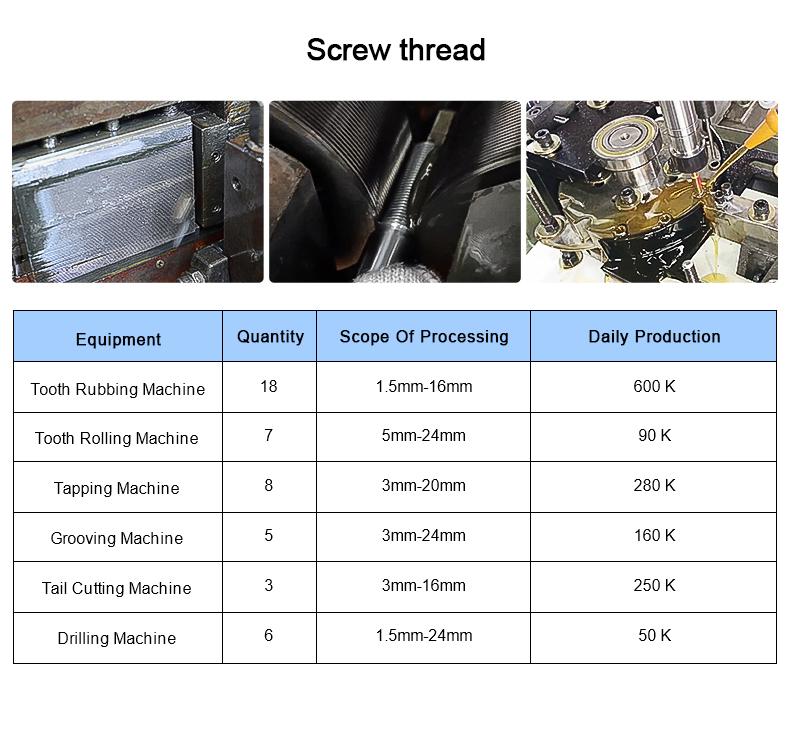
O processo de encabeçamento a frio é um dos novos processos para a maquinagem sob pressão com menos ou nenhum corte
metal. É um método de processamento que utiliza a deformação plástica do metal sob a ação de
forças externas e, com a ajuda de moldes, redistribui e transfere o volume de metal para formar
as peças ou os espaços em branco necessários. O processo de encabeçamento a frio é o mais adequado para a produção de
elementos de fixação, tais como cavilhas, parafusos, porcas, rebites, cavilhas, etc.
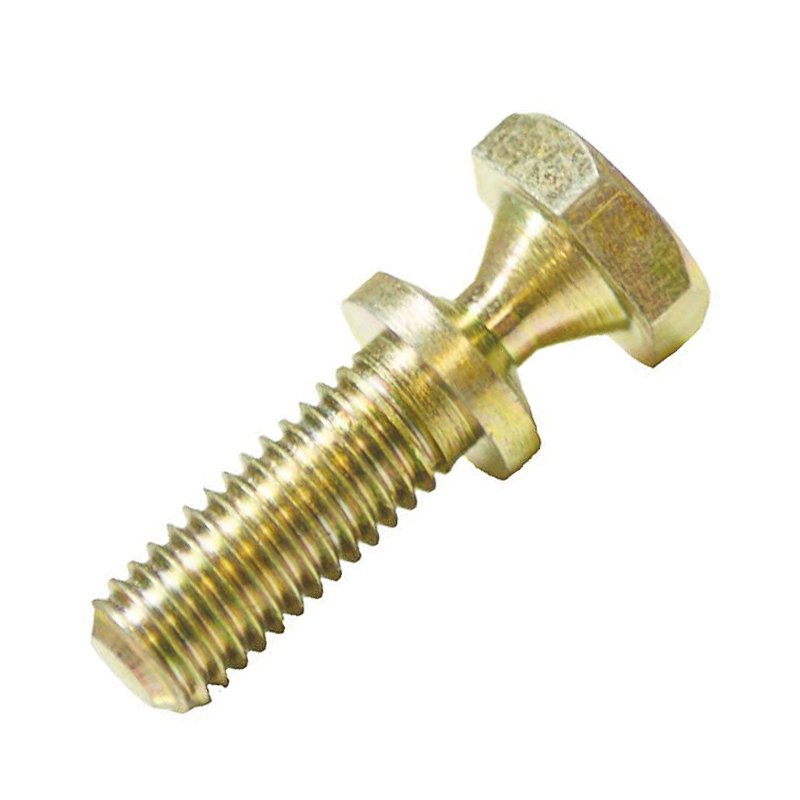
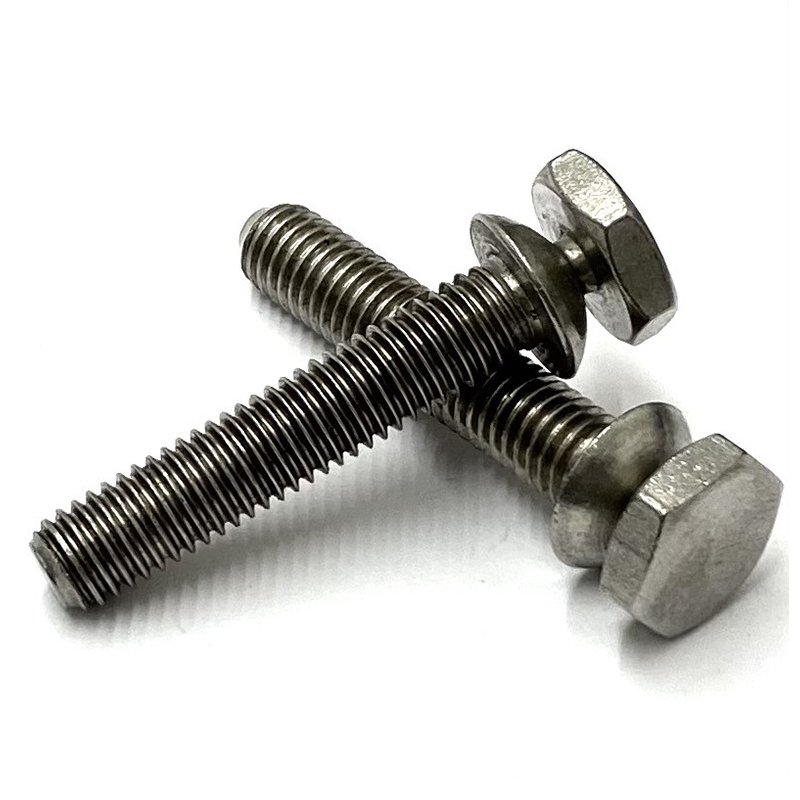
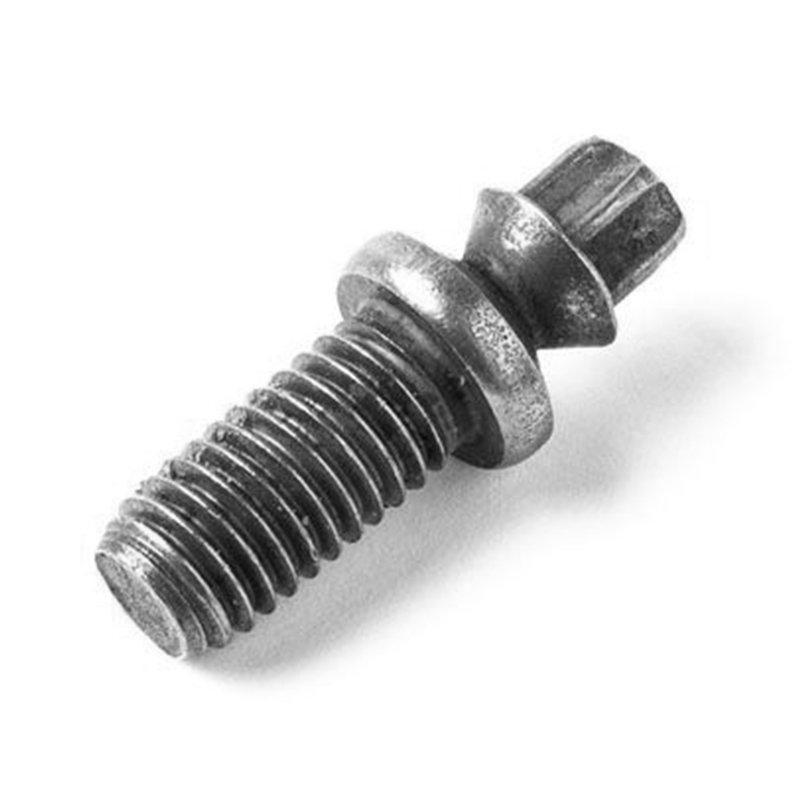
Escalonado parafusos de cisalhamento são fixadores especializados concebidos para proporcionar uma falha de corte controlada sob condições de carga específicas, frequentemente utilizados em aplicações estruturais ou mecânicas em que a segurança e os pontos de falha previsíveis são fundamentais. Eis uma descrição pormenorizada:
Principais caraterísticas dos parafusos de cisalhamento escalonados:
-
Design de veio escalonado
-
O parafuso tem um secção de diâmetro reduzido (ranhura de cisalhamento) ao longo da sua haste, criando um ponto fraco deliberado.
-
Este passo assegura o corte do parafuso com uma carga pré-determinada, protegendo outros componentes de danos.
-
-
Material e resistência
-
Normalmente fabricado com aço de alta resistência (por exemplo, Grau 5, Grau 8 ou liga de aço) para garantir um desempenho de corte consistente.
-
Tratada termicamente para uma resistência ao corte precisa.
-
-
Tipos de cabeça
-
Disponível em várias cabeças (hexagonal, de encaixe, redonda), consoante as necessidades da aplicação.
-
Alguns modelos incluem um cabeça separadora que se solta após um binário de instalação adequado.
-
-
Tipo de rosca
-
Caraterística de maio enfiamento total ou parcialO passo de corte está localizado na parte não roscada para evitar a distorção da rosca durante o corte.
-
-
Controlo da carga de cisalhamento
-
A secção escalonada é concebida para falhar com uma força de corte específica, actuando como um fusível mecânico.
-
Utilizado em sistemas críticos de segurança (por exemplo, aeronaves, máquinas, juntas estruturais) para evitar sobrecargas.
-
Aplicações:
-
Engenharia de estruturas: Ligações críticas ao corte em estruturas de aço.
-
Aeroespacial: Pinos de cisalhamento em sistemas de controlo de voo.
-
Automóvel: Componentes da suspensão ou do sistema de tração.
-
Maquinaria industrial: Proteção contra sobrecargas em acoplamentos ou caixas de velocidades.
Vantagens:
-
Fracasso previsível: Evita danos catastróficos por cisalhamento a uma carga definida.
-
Substituição fácil: Os parafusos partidos podem ser rapidamente substituídos após a falha.
-
Resistência à corrosão: Muitas vezes revestidos (por exemplo, zinco, cádmio) para maior durabilidade.
Exemplo de caso de utilização:
Num turbina eólicaOs parafusos de corte escalonados podem fixar o cubo da pá. Se ocorrer uma força excessiva (por exemplo, ventos tempestuosos), os parafusos cortam-se, protegendo o conjunto do rotor de danos graves.







Avaliações
Ainda não existem avaliações.