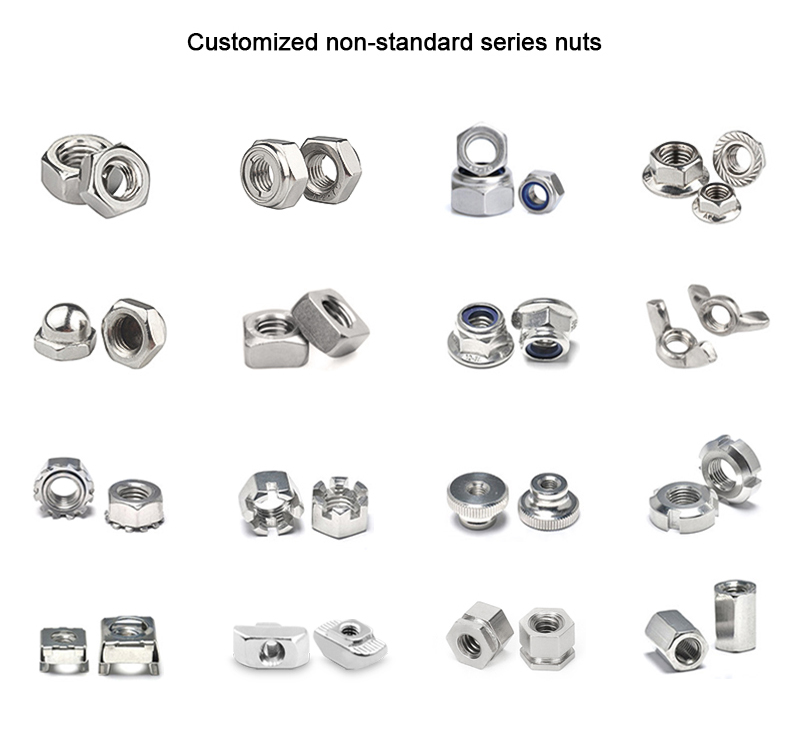
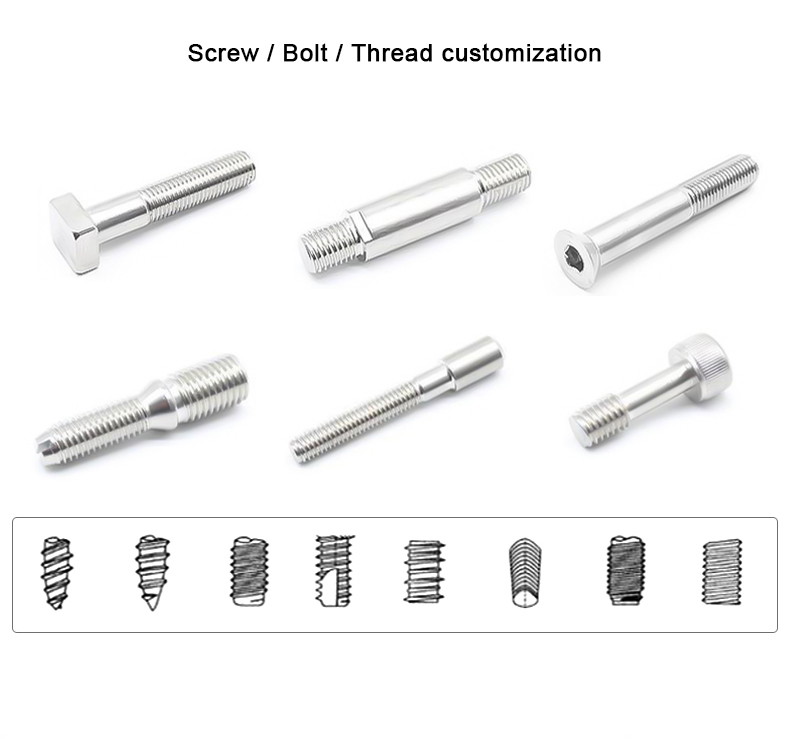




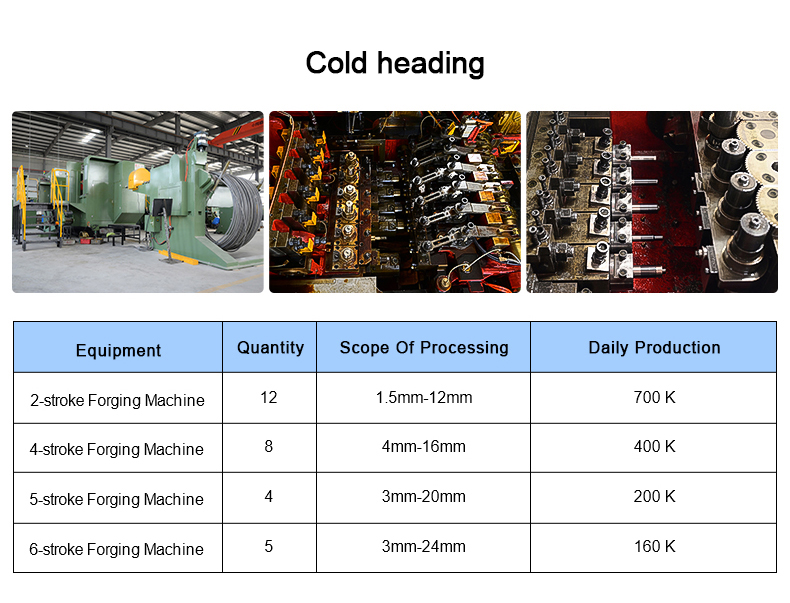
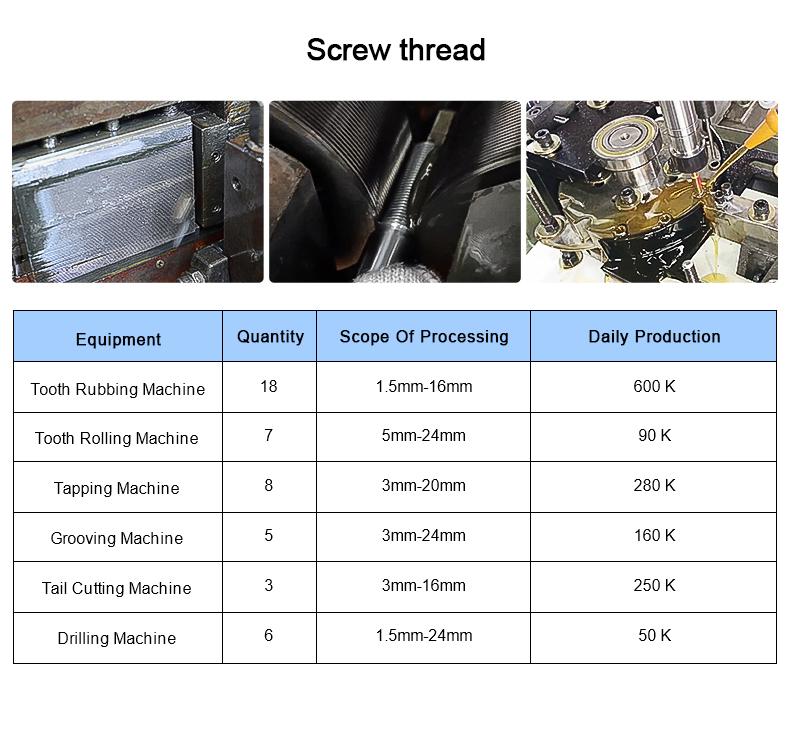
Cold heading process is one of the new processes for pressure machining of less or no cutting
metal. It is a processing method that utilizes the plastic deformation of metal under the action of
external forces, and with the aid of molds, redistributes and transfers the volume of metal to form
the required parts or blanks. The cold heading process is most suitable for producing standard
fasteners such as bolts, screws, nuts, rivets, and pins.etc
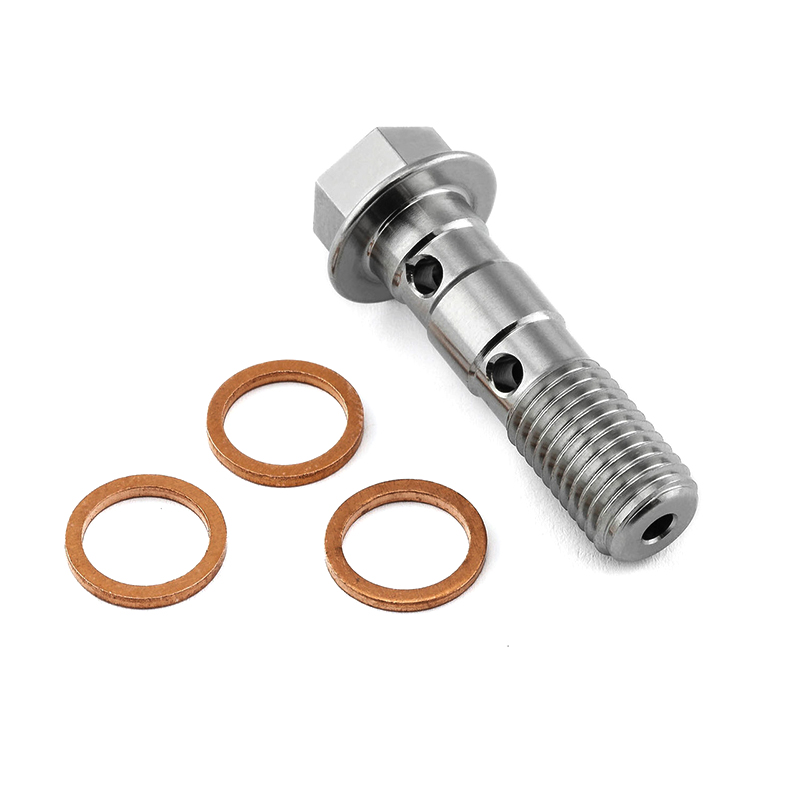
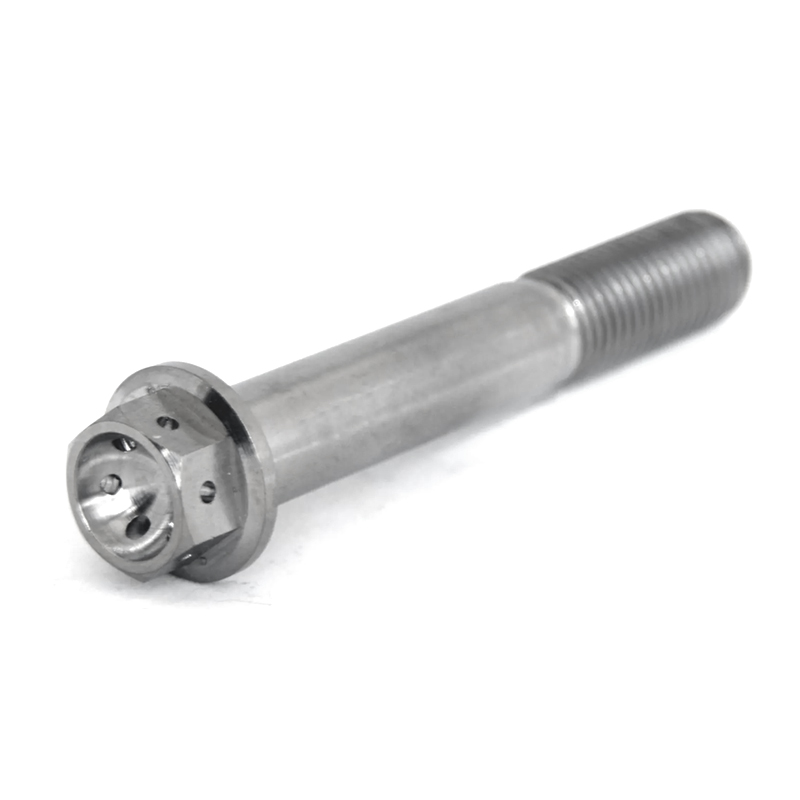
Safety wire bolts, also known as lock-wire bolts or drilled head bolts, are specialized fasteners designed to be secured with safety wire (lock wire) to prevent loosening due to vibration or rotation. These bolts are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, motorsports, and other high-performance applications where reliability is critical.
Bolt Plating for Safety Wire Bolts:
Plating is applied to safety wire bolts to enhance corrosion resistance, reduce friction, improve appearance, and sometimes to meet specific conductivity or thermal requirements. Common plating options include:
1. Cadmium Plating (Cad)
-
Properties: Excellent corrosion resistance, good lubricity, and sacrificial protection.
-
Appearance: Yellowish-silver.
-
Common Use: Aerospace and military applications (though being phased out due to environmental concerns).
-
Limitations: Toxic, restricted under RoHS and REACH regulations.
2. Zinc Plating (Zn)
-
Properties: Good corrosion resistance, cost-effective.
- Common Use: Automotive, industrial, and general-purpose applications.
-
Limitations: Less durable than cadmium in harsh environments.
4. Chrome Plating (Cr)
-
Properties: Extremely hard, excellent wear resistance, decorative.
-
Appearance: Mirror-like shine.
-
Common Use: High-performance engines, marine applications.
-
Limitations: Can be brittle and prone to chipping.
- Safety wire bolt plating
Selection Considerations:
-
Environment: Marine or high-humidity applications may require cadmium or nickel.
-
Regulations: Cadmium is restricted in many industries; alternatives like zinc-nickel are preferred.
-
Temperature: Nickel and chrome handle high heat better than zinc.
-
Aesthetics: Chrome and nickel provide a polished look, while black oxide or zinc offers a matte finish.
Conclusion:
The choice of plating for safety wire bolts depends on the application’s mechanical, environmental, and regulatory requirements. Aerospace often uses cadmium or zinc-nickel, while automotive and industrial applications may opt for zinc or phosphate coatings. Always verify industry standards (e.g., ASTM, MIL-SPEC) when selecting plating for critical applications.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.