


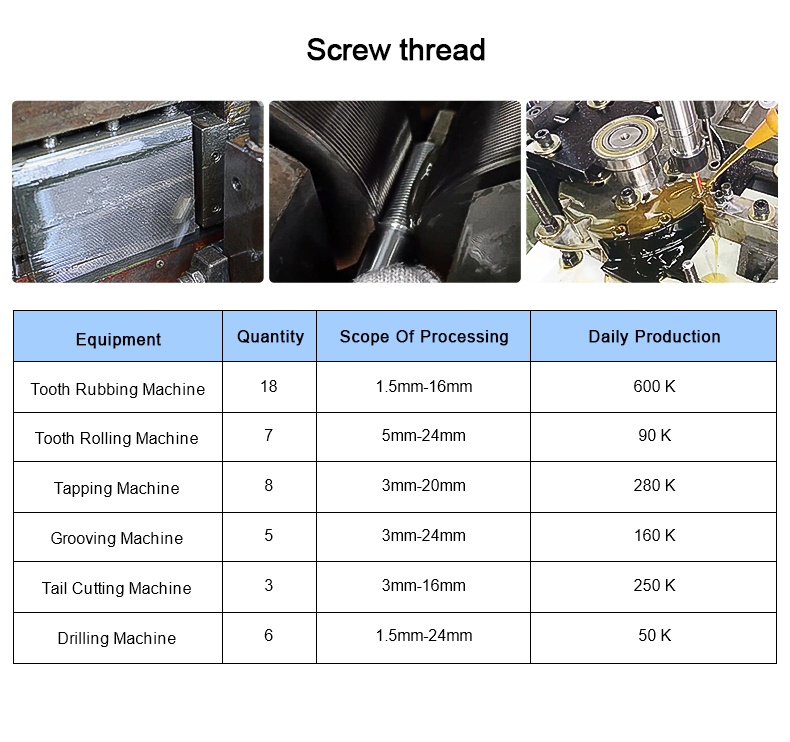
Cold heading process is one of the new processes for pressure machining of less or no cutting
metal. It is a processing method that utilizes the plastic deformation of metal under the action of
external forces, and with the aid of molds, redistributes and transfers the volume of metal to form
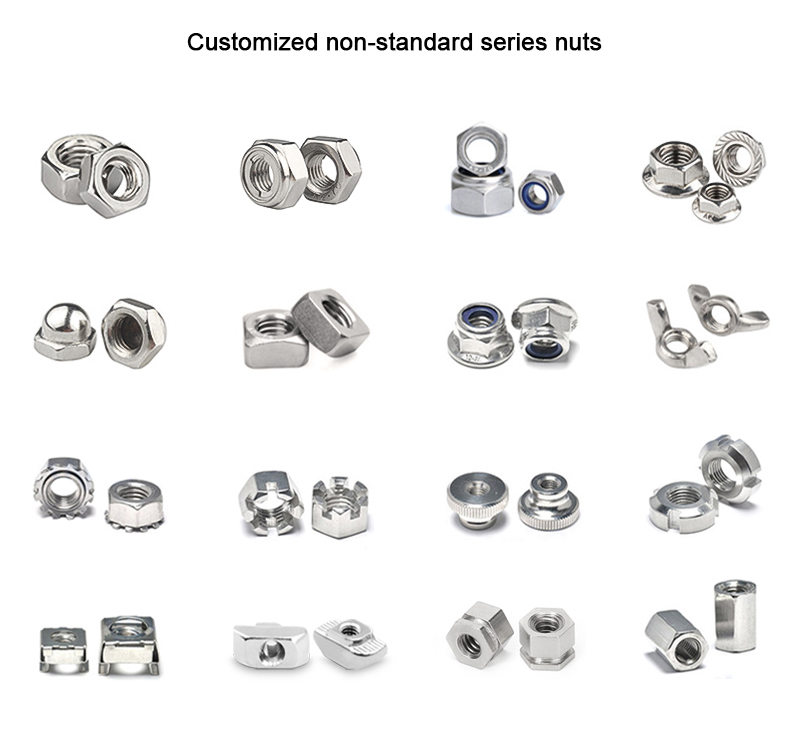
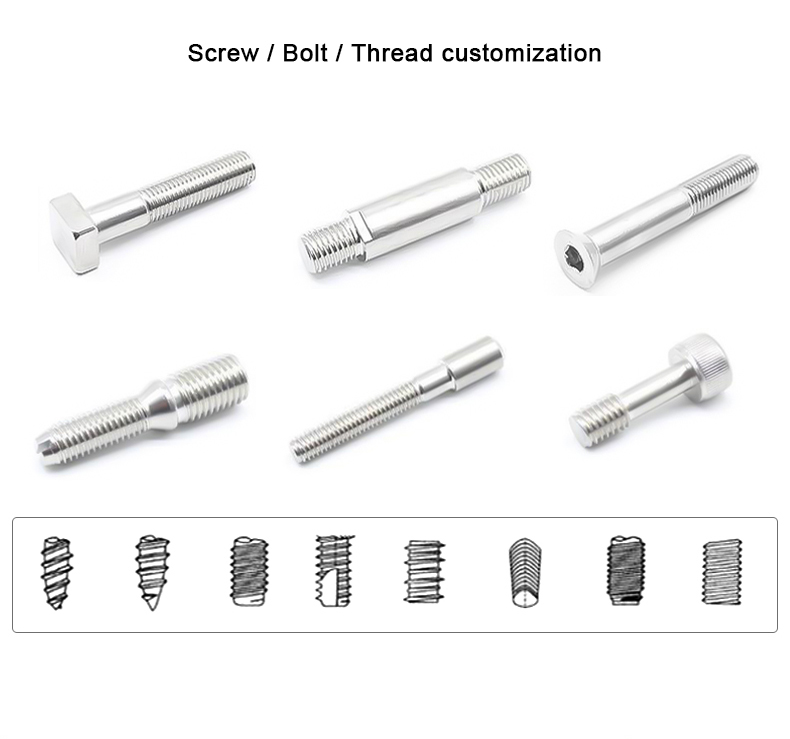
the required parts or blanks. The cold heading process is most suitable for producing standard
fasteners such as bolts, screws, nuts, rivets, and pins.etc

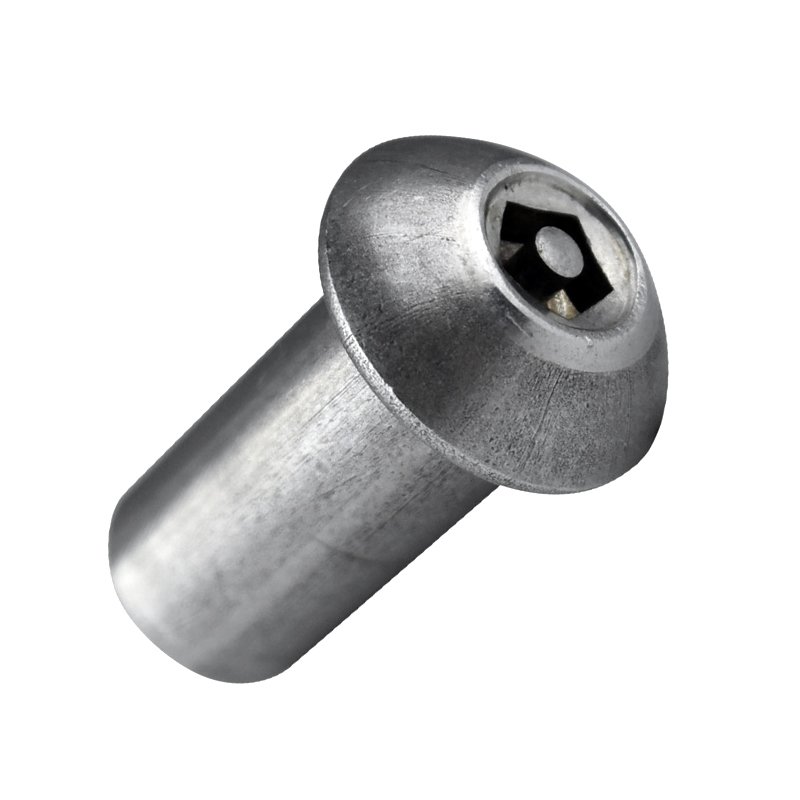
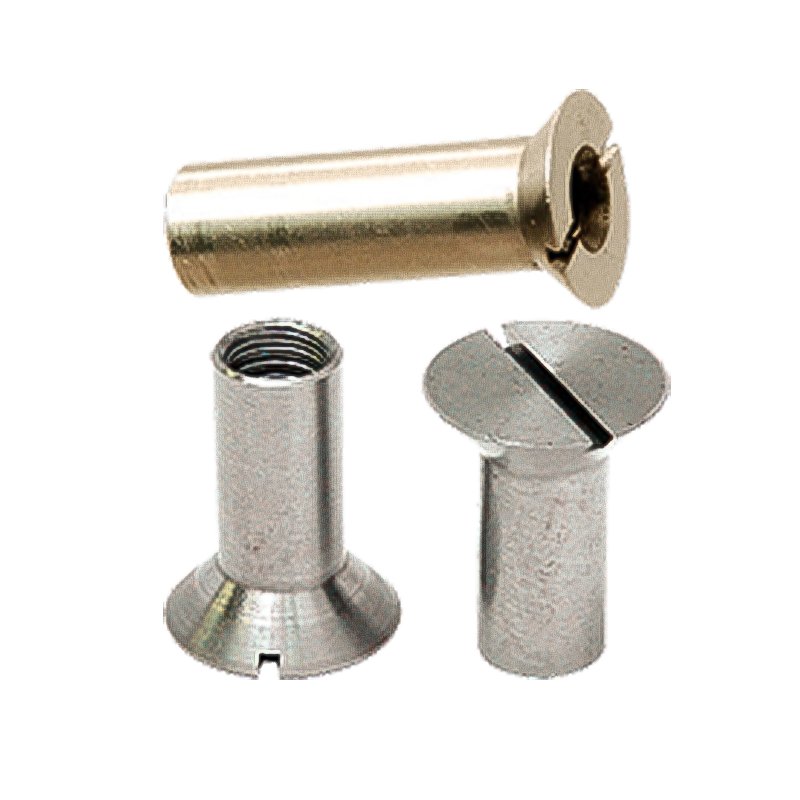
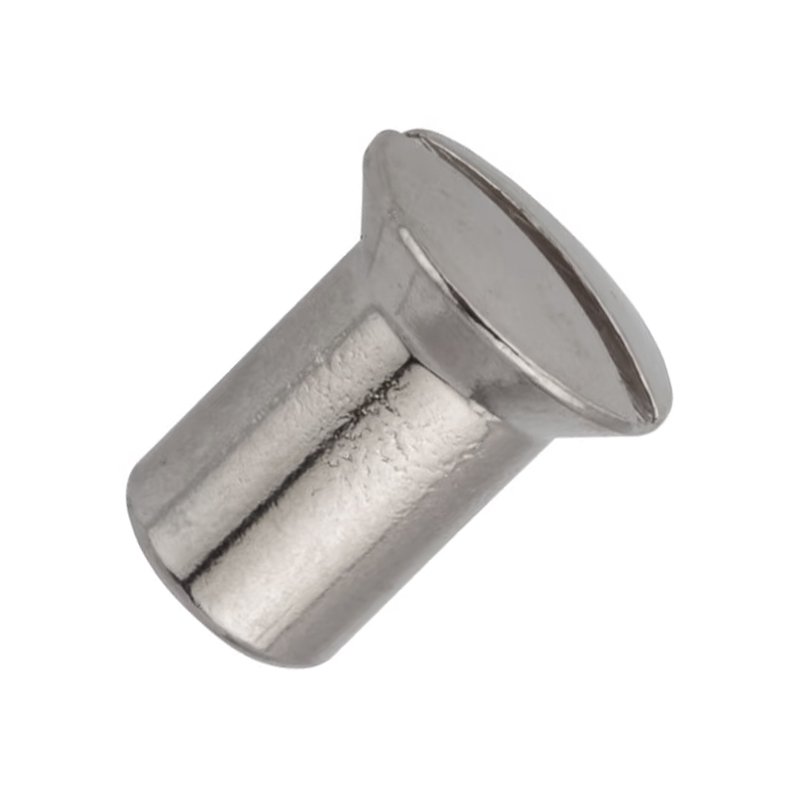
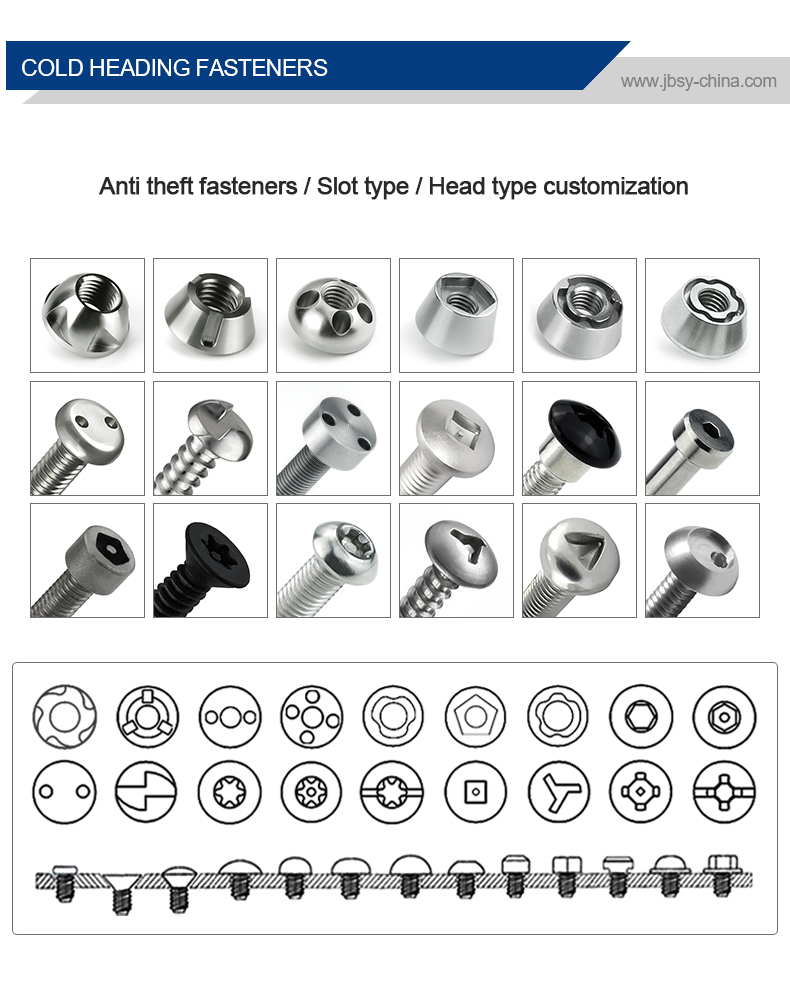
A flat head barrel nut is a type of fastener designed for specific applications where a low-profile, countersunk connection is needed. Here’s a detailed description:
Features:
-
Flat Head Design – The nut has a conical (tapered) underside that allows it to sit flush with the surface when installed in a countersunk hole.
-
Barrel Shape – The body of the nut is cylindrical (barrel-shaped), often with internal or external threading.
-
Thread Type – Typically features internal threads (female threads) to accept a matching bolt or screw.
-
Material – Commonly made from steel (carbon or stainless), brass, or aluminum, depending on strength and corrosion resistance needs.
-
Drive Type – May include slots for a screwdriver, a hex socket, or another drive mechanism for installation.
-
Finish – Can be plain, zinc-plated, black oxide, or coated for corrosion resistance.
- Flat head toothed barrel nut
Common Uses:
-
Countersunk Fastening – Used in applications where a smooth, flush surface is required (e.g., furniture, automotive panels, aerospace components).
-
Barrel Nuts in Furniture – Often found in flat-pack furniture (like IKEA) for hidden, sturdy joints.
-
Machinery & Automotive – Used in assemblies where space is limited and a low-profile fastener is necessary.
Advantages:
-
Provides a sleek, flush finish.
-
Distributes load efficiently due to the tapered seat.
-
Helps prevent snagging in moving parts.
- Flat head toothed barrel nut
Disadvantages:
-
Requires a countersunk hole, which may need precise machining.
-
May have lower torque resistance compared to standard hex nuts.






